Security and Disclosure
qs-jwt is open source and you have access to all source code.
It is your own responsibility to determine if qs-jwt is suitable for your use case. The creators of qs-jwt, including Ptarmigan Labs, Göran Sander or any other contributor, can and must never be held liable to past or future security issues of qs-jwt. If you have security concerns or ideas around qs-jwt, please get involved in the project and contribute to making it better!
Security Disclosure
If you discover a serious bug with qs-jwt that may pose a security problem, please disclose it confidentially to security@ptarmiganlabs.com first, so it can be assessed and hopefully fixed prior to being exploited.
Please do not raise GitHub issues for serious security-related doubts or problems.
Virus Scanning
Every time a qs-jwt release is done the created binaries are sent to VirusTotal for scanning.
VirusTotal acts as an aggregated virus scanner that sends the qs-jwt binaries to dozens of anti-virus scanners, including many of the major, established ones.
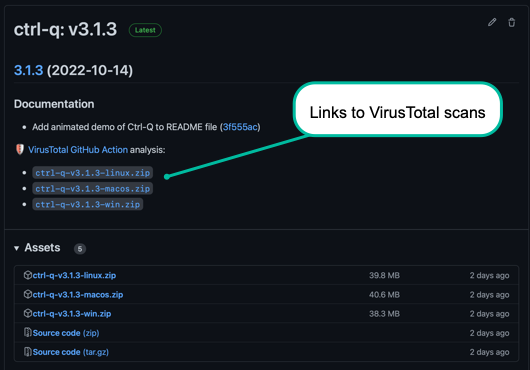
Links to the VirusTotal scan report are included in each release notes, making it easy to check the status of each binary:
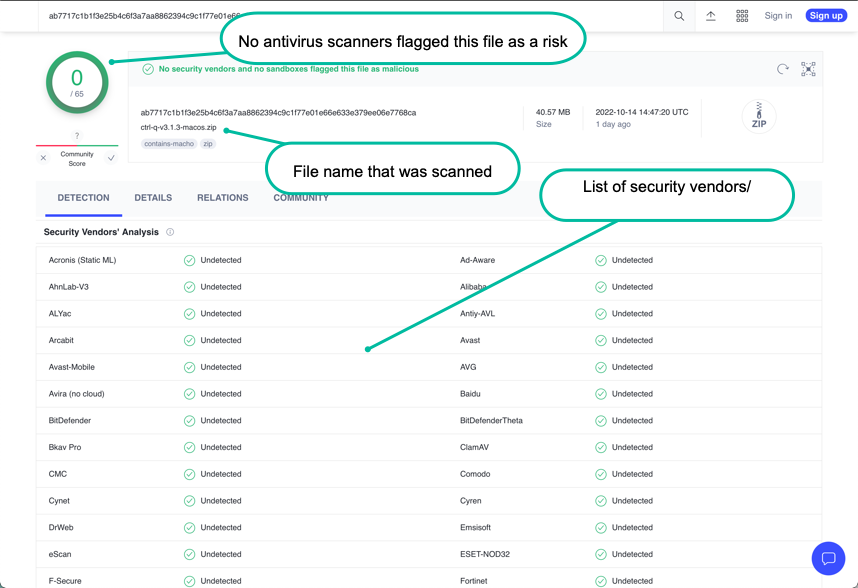
A VirusTotal scan that reports "no risks found" can look like this:
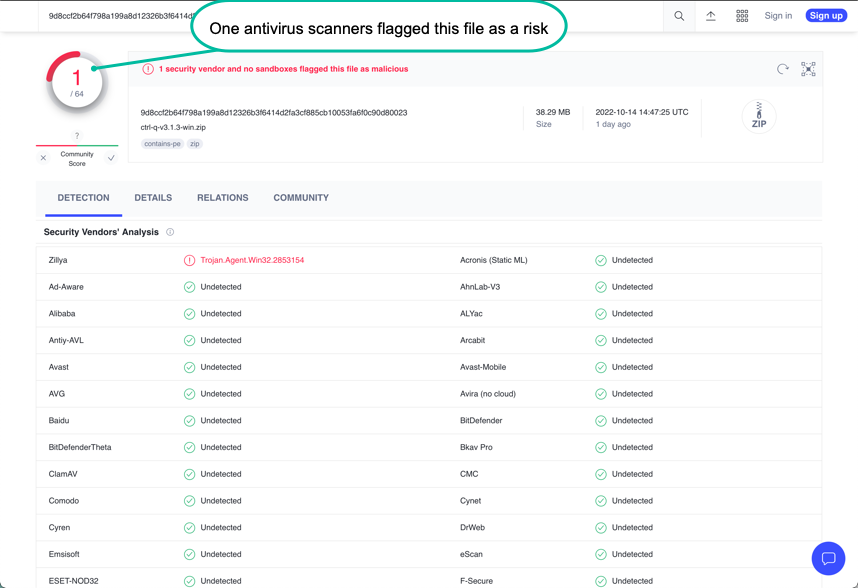
Positive scan vs false positives
If one or more of the security vendors used by VirusTotal reports an issue you have to make a decision.
Is it a real issue or a false positive?
You have to decide this yourself, but some general lines of thought can be:
Is it a single vendor that reports the qs-jwt binary file to be a risk, or several vendors? If one vendor reports an issue and 60+ vendors don't, you might be looking at a false positive.
But again - at the end of the day it's you that must make that decision.
A scan where a single security vendor reports an issue can look like this:
Signed Binaries
The macOS executable binary is signed and notarized by Apple's standard process.
A warning may still be shown first time the app is started. This is expected and normal.
The Windows executable binary is signed by "Ptarmigan Labs AB".
JWT Security Considerations
JWT Data Exposure
Important
JWTs (when used with Qlik Sense) contain unencrypted information about users and provide access to the Qlik Sense system. In other words: Qlik Sense JWTs should be treated just like user IDs and passwords.
Key security points about JWTs:
- Not Encrypted: JWT data can be read by anyone who intercepts the token
- Cryptographically Signed: Cannot be modified without detection
- Time-Limited: Use short expiration times as a security best practice
- Revocation: Once created, JWTs cannot be revoked until expiry
Best Practices
JWT Handling
- Use HTTPS: Always transmit JWTs over encrypted connections
- Short Expiration: Keep JWT validity periods short (hours/days, not months)
- Secure Storage: Store JWTs securely, never in plain text files or logs
- Minimal Claims: Only include necessary information in JWT claims
Certificate Management
- Protect Private Keys: Never commit private keys to source control
- Key Rotation: Rotate signing certificates regularly
- Key Storage: Use secure key management systems in production
- Access Control: Limit who can access signing keys
Operational Security
- Monitoring: Monitor JWT usage and expiration
- Logging: Be careful about what JWT-related information is logged
- Environment Separation: Use different certificates for different environments
- Documentation: Maintain clear documentation of JWT policies and procedures
Development Security
Source Code
- All source code is available on GitHub
- Code is regularly reviewed and updated
- Community contributions are welcome and reviewed
- Issues and security concerns can be reported through GitHub
Dependencies
- qs-jwt uses well-established, maintained libraries
- Dependencies are regularly updated for security patches
- Dependency scanning is performed as part of the build process
Build Process
- Builds are automated and reproducible
- Binary artifacts are scanned before release
- Release process includes security checks
Compliance Considerations
Data Privacy
- JWTs may contain personal information (names, emails)
- Consider GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy regulations
- Implement appropriate data handling procedures
- Document JWT data flows and retention policies
Audit Requirements
- Log JWT creation and usage events
- Maintain records of certificate management
- Document security procedures and policies
- Regular security reviews and updates
Industry Standards
- Follow JWT best practices (RFC 7519)
- Implement proper certificate management
- Use appropriate cryptographic standards
- Regular security assessments
Security Resources
Qlik Security
JWT Security
General Security
Reporting Issues
Security Issues
- Critical security issues: Email security@ptarmiganlabs.com
- General security questions: Use GitHub Discussions
- Non-security bugs: Use GitHub Issues
Response Process
- Assessment: Security reports are assessed within 48 hours
- Investigation: Detailed investigation of confirmed issues
- Fix Development: Patches developed and tested
- Coordinated Disclosure: Security advisory and patch release
- Follow-up: Verification and additional measures if needed