QSEoW: Using JWTs in Security Rules
Any claim embedded in the JWT can be used in QSEoW security rules.
The claims are available as user.environment.<claim name> in the security rules.
You must write the security rule manually in the Conditions text box (i.e. the authoring tool doesn't work for JWT claims).
Example Security Rule
A rule that gives access to a specific stream for all JWTs where the group claim is "group 2" can look like this:
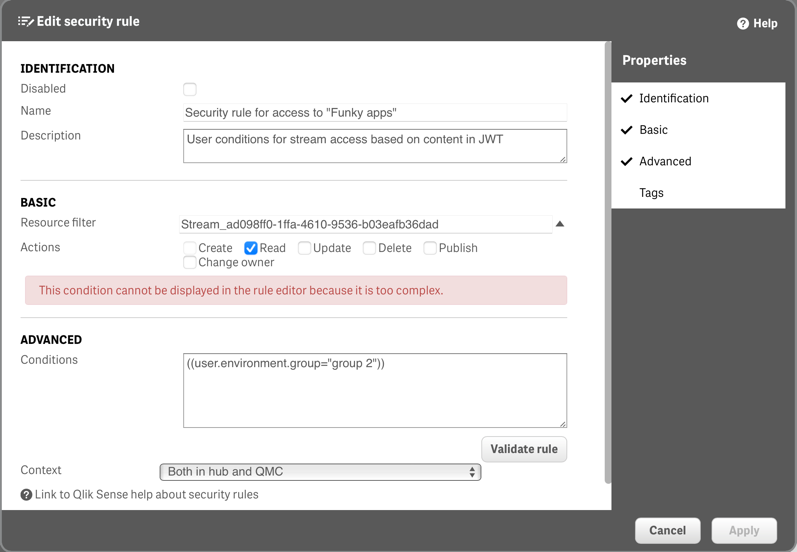
Available JWT Claims
When you create a JWT using qs-jwt, the following claims are available in security rules:
Standard Claims
user.environment.userId- The user ID from--useriduser.environment.userDirectory- The user directory from--userdiruser.environment.name- The display name from--usernameuser.environment.email- The email address from--useremail
Group Claims
Groups specified with --groups are available as arrays:
user.environment.group- Array of all groups
Example Security Rule Conditions
Grant access based on user directory
javascript
user.environment.userDirectory = "COMPANY";Grant access based on group membership
javascript
user.environment.group.indexOf("admin") >= 0;Grant access based on email domain
javascript
user.environment.email.indexOf("@company.com") >= 0;Complex rule combining multiple claims
javascript
(user.environment.userDirectory = "COMPANY" and user.environment.group.indexOf("power-users") >= 0)
or user.environment.group.indexOf("admin") >= 0Security Rule Types
JWT claims can be used in various types of security rules:
Stream Access
Control which streams users can access based on JWT claims.
App Access
Grant or deny access to specific applications.
System Access
Control access to QMC, Hub, or other system components.
Best Practices
Principle of Least Privilege
- Only include necessary claims in JWTs
- Design security rules to grant minimal required access
- Regularly review and update security rules
Group-Based Access
- Use groups rather than individual user IDs where possible
- Maintain consistent group naming conventions
- Document group purposes and access levels
Testing Security Rules
- Test security rules with different JWT configurations
- Verify that rules work as expected in development before deploying
- Document security rule logic and dependencies
JWT Claim Design
- Use meaningful group names that reflect organizational structure
- Include role-based claims when appropriate
- Consider future scalability when designing claim structure
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
- Claims not available: Ensure claims are properly included in JWT creation
- Case sensitivity: JWT claims are case-sensitive in security rules
- Array handling: Remember that groups are arrays, use
indexOf()to check membership - Special characters: Be careful with special characters in claim values
Debugging Tips
- Use the Security Rule Debugger in QMC to test rules
- Check JWT contents using online JWT decoders (development only!)
- Start with simple rules and gradually add complexity
- Log security rule evaluation for troubleshooting
Security Considerations
JWT Security
- JWTs contain unencrypted data - treat them as credentials
- Use short expiration times to limit exposure
- Rotate signing certificates regularly
- Never include sensitive data in JWT claims
Security Rule Security
- Regularly audit security rules for correctness
- Test security rules thoroughly before deploying
- Maintain documentation of security rule logic
- Consider the impact of security rule changes on existing users